Even though mortgage, pledge, hypothecation, and charge are terms used by financial institutions to provide you a loan secured by your assets, it is important that you know that they differ from each other. So, read on to learn about the differences between these terms and make a more informed choice when the time comes.
- Charge
A charge is simply the term used to define the right or ownership that a lender has over an immovable or movable asset of yours when you take a loan. Charges are created by lenders in three ways when extending a loan to you: mortgage, pledge or hypothecation.
- Mortgage
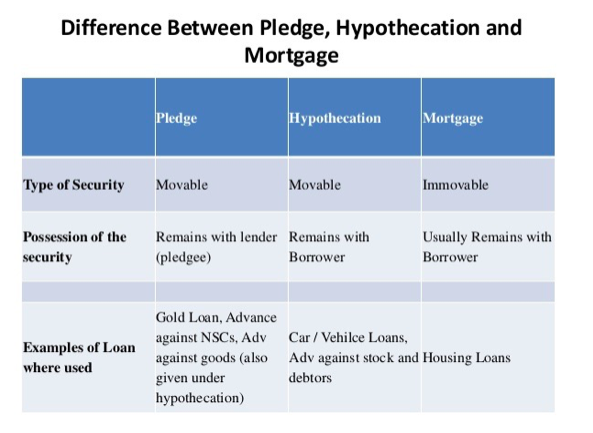
A mortgage is a legal contract between you and the lender that allows you to borrow money by mortgaging your immovable property such as land or an apartment. Mortgage assures the lender that you will not delay or default in repayment of your loan. In the off-chance that you do, they have your property as a guarantee to recover the loan amount. Your lender can seize and sell your property in case of default. However, possession of the property remains in your hands which means you can reside in the home even after you mortgage it while repaying the loan.
- Pledge
When your lender actually takes possession of movable securities such as certificates or goods it is known as a pledge. The lender has the right to possess these securities until you repay the entire amount. Also, they have the right to sell these securities in case you default, to recover the total amount due. Some of the best examples of the pledge are jewelry loans, gold loans, advance against stocks and others.
- Hypothecation
Hypothecation is similar to a mortgage, only here the asset is movable, such as a two-wheeler in a vehicle loan. In this case, the two-wheeler will be in your possession, so if the need arises, the lender will first have to take possession of the asset, that is the two-wheeler, and can then proceed to sell it when you default on loan repayment.
After learning the basic difference between charge, mortgage, pledge, and hypothecation, you can choose a loan option on the basis of what you’re more comfortable with. In an instance where you need substantial funds and wish to pay nominal interest rates for a borrowed sum, it makes the best sense to choose a loan against property, where you get a hefty sanction against any commercial or residential property that you own.
To avail a loan up to Rs.3.5 crore if you are self-employed and up to Rs.1 crore, if you are a salaried person, you can apply for a Bajaj Finserv Loan Against Property. Here you can benefit from a flexible repayment tenor ranging from 2 to 20 years if you are salaried, and up to 18 years if you are self-employed. However, before you apply for a loan against property in India, check your pre-approved offer from Bajaj Finserv. It is the simplest and fastest way to access the amount that you need!