Table of Contents
What square can measure the normal blood sugar level?
The normal blood sugar level is the key to measuring overall health and the body's ability to function normally every day for those individuals with polygenic infections, an effort to acknowledge that normal blood sugar levels may be a continuous, hour-by-hour pursuit. Besides, it is not primary.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nWgf-odA50Q
This article will explore the "normal" blood glucose levels and target ranges for non-diabetic patients, as well as reasonable blood glucose targets for people with type 1 diabetes and type 2 polygenic infections.
Typical normal blood sugar for stable non-diabetic patients
For people who do not have a polygenic disease type, blood sugar levels are usually calculated once an hour, generally between 70 and 130 mg/dL, and the same is valid for the last dinner. More recent hypotheses about non-diabetic blood glucose levels have brought blood glucose levels as high as 140 mg/dL after the feast.
(Once you have the opportunity to live outside the United States and adapt to the square measurement, quantify in mmol/L, separate all numbers by 18)
Here, it should be synchronized with the Yankee Polygenic Disease Association to measure the range of average blood glucose at a single time, not polygenic infections:
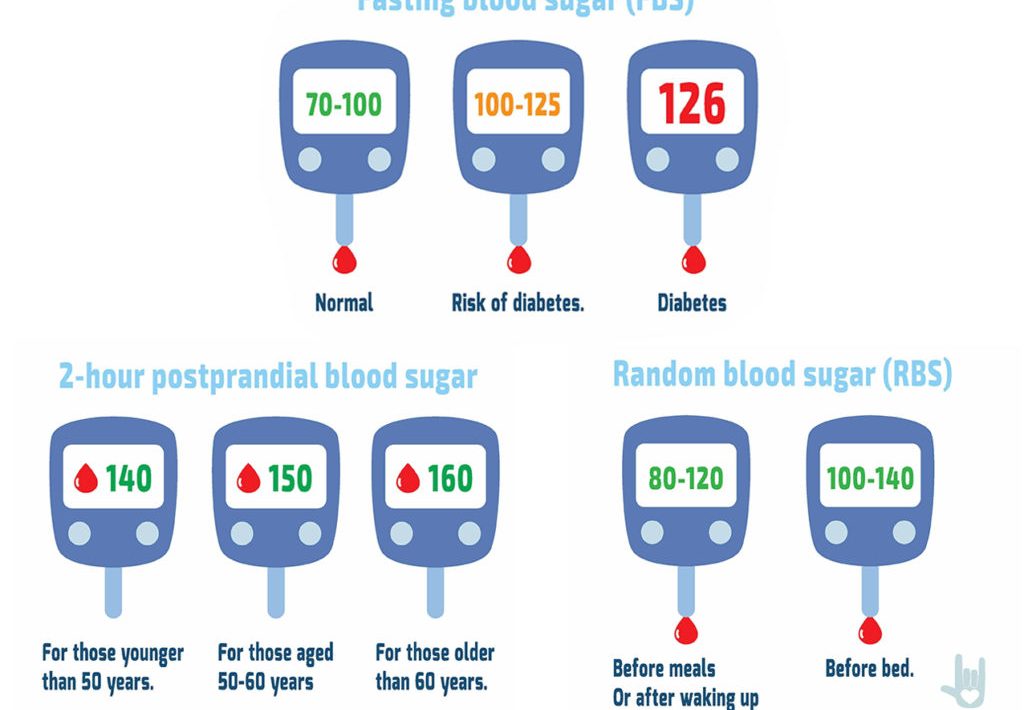
Fasting normal blood sugar
(the first part of the meal eaten the day before): less than 100 mg/dL
Supper 1 hour: 90 to 30 mg/dL
Dinner for 2 hours: 90 to 110 mg/dL
5 tons at a time or one hour: 70 to 90 mg/dL
Diagnosis of type 2 prediabetes and classified as a normal blood sugar
Depending on the country or clinical association you are proposing, the passing rate of "typical" vs. "pre-diabetes" to the analyzed type I or type II polygenic diseases will vary. The subsequent squared measurement of blood glucose and A1c final result is adapted to the analyzed pre-diabetes and polygenic disorders, and the relevant information is synchronized with the Yankee Polygenic Disease Association of the United States and the British Polygenic Infection:
Pre-diabetes
HbA1c: 5.7% to 6.4%
Fasting: 100 to 100 25 mg/dL
Dinner for 2 hours: 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL
Enter several polygenic diseases
HbA1c: 6.5 p.c or higher
Fasting: 126 mg/dL or higher
A feast for 2 hours: two00 mg/dL or higher
Please note: Sorting a polygenic disease usually proliferates. This suggests that when a squared amount is felt, the blood sugar level will usually remain stable above 200 mg/dL. For some people, these symptoms will recover quickly along these lines because they are waiting for respiratory disease or another apparent typical infection.
When measuring the blood glucose level, some newly analyzed patients can see blood glucose levels exceeding 400 mg/dL or higher. If the chance you are doing is to speculate that you or your friends or family members have some polygenic infection, please immediately consider your clinical considerations or seek help. You are welcome to perform a live ketone test on the water to test blood sugar levels and A1c.
Your A1c and normal blood sugar indicators
Dealing with any polygenic infection is much higher than giving patients some chemicals and advising them to keep their blood sugar in X and X. If you have been suffering from a polygenic disease for a few days, you have undoubtedly realized this now.
What is A1c?
"A1c, Hb A1c, HbA1c, or glycosylated hemoglobin studies (various names of all comparable names) can be used as a biopsy to measure your normal blood glucose levels in the past 2-3 months," Christel Oerum in the DiabetesStrong brochure clarified the reduction of A1c Methods.
Before attempting to use A1c blood, the past blood sugar level schedule will significantly impact your results. In any case, the body's aldbiose related to Hb (the large molecule in red platelets) has been the amount. High blood sugar levels will produce a large amount of aldose hexose in your blood, among which a large amount of aldose hexose is related to hemoglobin.
Explain your A1c based on normal blood sugar levels
With this compound's basic adder, you can choose to interpret the most advanced A1C results to correlate "eAG" or "normal aldose levels."
Once you strive to support A1c and reach close to normal blood sugar levels, you can use this explanation. If you think that the partner A1c of vi.5 is classified as a moderate blood glucose level of 126 mg/dL or 100 to 152 mg/dL, then you can choose to study the flowing blood glucose results on your CGM and meter and point out that you are usually Which time of day is most important.
12% = 298 mg / dL or a difference of 240 – 347
11% = 269 mg / dL or a difference of 217 – 314
10% = 240 mg/dL or a change of 193 – 282
9% = 212 mg/dL or a change of 100 70 – 249
8% = 183 mg / dL or change 147 – 217
7% = 154 mg/dL or change 123 – 185
6% = 126 mg/dL or change 100 – 152
5% = 97 mg / dL or change 76 – 120
In non-polygenic infections, "normal blood sugar levels" {in one partner, uncommonly many in one partner}} individuals may cause A1c as low as 4.6% or 4.7p.c, and as high as 5.6%.
Only 10 or 2 years have passed, and it is entirely uncommon for people with a polygenic disease to admit their partner A1c under vi p.c. Given the continuous improvement of chemical technology and the constant innovation of aldohexose sugar screening and more sensitive chemical siphon technology, many people with polygenic diseases are ready to achieve A1c levels in shifts above 5 o'clock safely.
Why your A1c is important
More or less: Your A1c is a clear sign of almost all the dangers that may cause polygenic tangles, such as pathology (grip and nerve damage in the feet), retinopathy (eye nerve damage, visual gambling impairment), kidney Insufficiency (neural damage to the kidneys), and severe illnesses in any part of the body that require rehabilitation.
For example, a small cut on the toe may cause gratitude for high blood sugar, fight it, and the related problems become severe enough that the disease may lead to its elimination.
The Yankee Polygenic Disease Association's overall index is to advocate partner A1c under the condition of not exceeding 7.0 p.c to deal with the inconvenience caused by polygenic infection. As A1c drops to near 6 pm, the risk of establishing the complexity of polygenic illness continues to decrease.
A small number of people with polygenic infections are concerned about A1c levels of 5 s or lower-especially those who have severe low carbohydrate withdrawal from food following the ketogenic diet and the author's diet. However, this has not been tried as a significant attempt in the investigation, and it is not feasible for people with polygenic infections.
It is also important to remember that your blood sugar level and A1c square are only a measure of the information disclosed to you, whether your body wants a ton or less of things, such as chemicals, multiple polygenic disease drugs, maintenance—the change of and the change of activities.
If your aldose analyzer or A1c result is not the same as the classification you see. Please use the type as inspiration to frame the changes (with the polygenic infection care team). No matter what, you can safely Deal with your polygenic disease to initiate different results.
Determine the correct A1c target for you
Because it is generally believed that a blood sugar change of 70 to 130 mg/dL is the best, this does not mean that your goals are different, especially if you have a polygenic infection or receive a chemical Drug for people with polygenic diseases in the second category.
So. the explanation for this may not be the right goal for you. Because the blood sugar levels in people taking chemicals. So, this are significantly lower, which is likely to bring about persistent hypoglycemia, which may be risky.
To achieve significant blood glucose levels, from 70 to 130 mg/dL, strict nutritional settings are usually required. And continuous blood glucose recognition is more than usual. Executives need precise medications. It takes a long time to learn your blood sugar level.
A1c target should be very close to home.
"The goal of A1c should be close to the family to maintain the individual's abilities, hazards, and past encounters," clarified the purpose of Scheiner, MS, and CDE to establish the father of comprehensive polygenic infection and the creator of an exocrine organ.
"For example, in general, we usually focus on an incredibly close to A1c level through our physical state. So, it have a lot of medium attention to younger children and more sophisticated people."
Nevertheless, Scheiner has some crucial factors, which may make people focus on the superior A1c. Similar to "hypoglycemia obviousness," once people with polygenic diseases do not feel the imminent signs of hypoglycemia, It can be said. After a seizure or passing, this may put you at serious risk of severe hypoglycemia. To reduce this harm, you will focus on a higher objective blood glucose range.
Scheiner added: “People with significant hypoglycemia. Also, meager backgrounds should aim for higher blood sugar levels than those whose low points are found and responded to by the UN office,” Scheiner added. "Of course, there is also a United Nations office that has been running A1c at a double-digit speed (for example, 10 o’clock or higher). Your time must never set the partner’s A1c target at 6%...higher to achieve Unassuming, wise potential target."
Blood sugar is not just a result of diet.
Traditional media will ask you to accept that your blood sugar level is the smallest squared. This depends entirely on your diet and rich exercise style. In any case, people with the first and second polygenic infections are frequently investigated by the UN Office. Blood sugar may leak anyway.
Once you have observed your blood sugar and goals. Also, maintaining this mentality becomes especially important because there are square-foot constraints. And difficulties affecting blood sugar levels, which you can never preserve.
E.g.:
Period: Increase blood sugar and chemical cravings
Serious competition, fierce competition, adrenaline surge caused by roller coaster: elevated blood sugar and chemical cravings
Respiratory diseases and various diseases: in some cases, it will increase blood sugar and chemical cravings
Hormonal changes in adolescent adults due to puberty and voice development: increased blood sugar and chemical cravings
A physical problem that usually leads to increased obesity: elevated blood sugar and chemical cravings
Glucose produced by anaerobic exercise: raising normal blood sugar
Although you basically cannot prevent these variables that affect blood sugar from occurring. Also, you can choose to cooperate with the polygenic disease care team to guide your chemistry. So, multiple polygenic infection drugs, maintenance of sex, and exercise levels to help them once they occur.
For example, once participating in muscle exercises such as anaerobic exercise. Also, many of us who suffer from a polygenic infection will notice that it is essential that they need to be small before muscle exercise or throughout their work. Dosage chemical bolus. Because muscle exercise will increase blood sugar.
Will it be stimulated with your blood sugar and A1c results?
Your blood sugar, chemicals, or medications all want to stay the same. If you gain weight or change the expression, your chemicals and drugs can be corrected. Once you have a lot of motivation or less motivation, your desire can be fixed. If you accidentally change your ability to maintain or desire little change, your passion will change!
In cooperation with your polygenic disease care team and polygenic disease director. So, the United Nations organization will show you the best way to determine your overall polygenic infection changes. The board of directors will formulate necessary measures. Polygenic infection maybe a learning strategy for abdominal burial.
Hold your breath and keep a low profile. If you don’t care what you see on the aldohexose table, don’t worry, don’t go crazy... please think about it! Make good records and work with the team to develop a framework to achieve the goal.