Understanding normal blood sugar level may be the key to self-management of polygenic diseases.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nWgf-odA50Q
This page lists the normal blood sugar level ranges and blood glucose ranges of adults and adolescents with polygenic diseases. There are several polygenic diseases. And blood sugar people who can see people with polygenic infections.
Suppose people with polygenic diseases include blood glucose meters. Check the test strips and try. Then it is essential to understand the recommendations for blood sugar levels.
The recommended glucose level has a certain level of translation for everyone, and you should check it with the steering group.
More importantly, young ladies can also set objective blood sugar levels through their physiological conditions.
The arrival area unit attached to the National Institute of Clinical Excellence (NICE) reminds that in any case, the termination scope of each person should be arranged by their primary care physician or diabetes consultant.
Table of Contents
The recommended target normal blood sugar level is reached.
NICE proposed a target glucose level regional unit for adults suffering from a polygenic disease. Several polygenic disorders and young people were suffering from a polygenic infection.
Moreover, the International Federation of Polygenic Diseases' goal is to achieve people's goals without explicitly pointing out polygenic infections.
This table provides general guidance. A personal goal set by your steering group is a goal you should focus on.
The recommended normal blood sugar level is reached.
Target level
Wake up before dinner type
(Before meal) At least one and a half hours at dinner
(After meal)
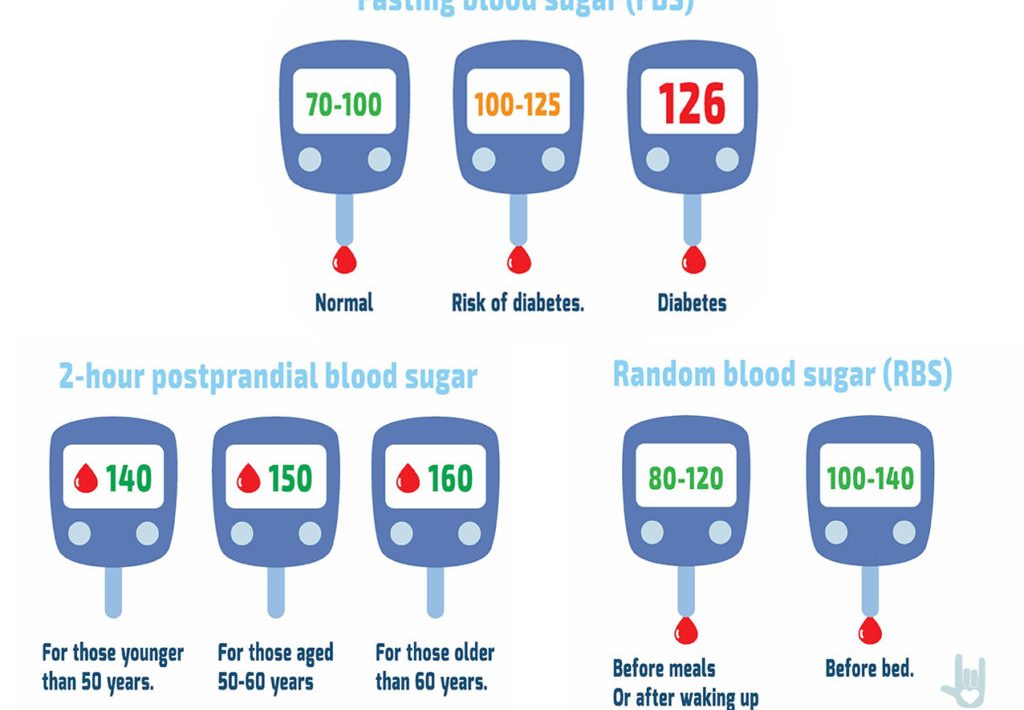
Non-diabetic* 4.0 to 5.9 mmol/L at 7.8 mmol/L
Enter a pair of diabetes of 4 to 7 mmol/L below 8.5 mmol/L
Type 1 diabetes 5 to 7 mmol/L 4 to 7 mmol/L 5 to 9 mmol/L
Children with one type of diabetes 4 to 7 mmol/L 4 to 7 mmol/L 5 to 9 mmol/L
*In any case, the non-diabetic digital area unit's information is not a NICE technique.
Typical and diabetic normal blood sugar level
For most non-disabled people, the regional units of blood sugar level are as follows:
Between 4.0 to 5.4 mmol/L (72 to 99 mg/dL) during rapid operation [361]
Up to 7.8 mmol/L (140 mg/dL) a few hours after admission
For people with polygenic diseases, the target area units for blood sugar levels are as follows:
Before dinner: 4 to 7 mmol/L for people with one or more polygenic infections
After dinner: less than nine mmol/L in patients with one polygenic disease, less than 8.5 mmol/L in patients with several polygenic diseases
Analyze normal blood sugar level in polygenic diseases
The following table lists the rules for judging polygenic diseases and prediabetes.
Blood glucose level measurement polygenic diseases
Plasma aldobiose detection of standard prediabetes diabetes
Any less than 11.1 mmol/l
Less than 200 mg/dl is not applicable 11.1 mmol/l or one ton.
200 mg/dl or one ton
Fasting is less than 5.5 mmol/l
Less than 100 mg/dl 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l
100 to 100 25 mg/dl 7.0 mmol/l or one ton
126 mg/dL or one ton
Less than 7.8 mmol/l 2 hours after a meal
Less than 100 40 mg/dl 7.8 to 11.0 mmol/l
140 to 199 mg/dl 11.1 mmol/l or one ton
200 mg/dl or one ton
Random plasma aldose hexose survey
At any time, a blood test with a blood plasma aldose hexose test may be required. Once the most typical situation, there is no need to worry about the most extreme summation plan, so it can be used to diagnose a polygenic disease.
Investigation of Fasting Plasma Aldose
When it is at least 8 hours fast, a quick check of plasma hexose aldose should be performed, and once in the morning.
NICE reminded that the immediate consequence of respecting the presumed plasma aldose hexose is 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l. The putter is at a higher risk of producing several polygenic infections once at various chances of causing multiple kinds of polygenic diseases—the centre of the factor.
Oral Aldose Tolerance Survey (OGTT)
Studies on the elasticity of oral glyoxal included starting with blood as an example, so taking a lovely drink containing 75g of glyoxal.
After drinking this beverage, you may have to stay still until a few hours later. You need to have an additional blood test.
HbA1c investigation of polygenic disease diagnosis
Although the HbA1c test did not directly increase the blood sugar level, in any case, your blood sugar level is too high or too low will affect the results for several months, thereby affecting the results of the investigation.
Under the result conditions, the signs of the normal blood sugar level or prediabetes area unit are given:
Normal: less than 42 mmol/mol (6.0%)
Pre-diabetes: 42 to 47 mmol/mol (6.0 to 6.4%)
Diabetes: 48 mmol/mol (6.5% or higher)
Why are the smart blood sugar levels of regional units significant?
It is essential that you only need to manage your blood sugar levels because you can choose blood sugar levels that are too high for a long time, which will increase the chance of polygenic diseases.
The complicated regional unit medical problems of diabetes include:
Kidney disease
Nerve damage
Retinal disease
heart disease
Stroke
In any case, the reduction of this problem seems to be ecstasy, and the most reasonable thing to see is that the possibility of those problems can be limited through smart glucose level management. Few upgrades will make your chances of staying firm and continuous improvement stand out in most situations.
Usually, once your normal blood sugar level or "aldose hexose in the blood" increases, for example, your duct organs will discharge the hypoglycemic specialist at dinner. This marks your body's absorption of aldose until its level falls back to normal levels.
In any case, if you have a polygenic infection,
your body will not build a hypoglycemic expert (a type of diabetes). Nor will it answer without exception (several types of diabetes). It may make your blood sugar too high for a long time. In the long term, this may damage nerves and veins and cause cardiovascular disease and various problems.
If you have a polygenic disease, your PCP may increase your blood sugar level by testing the blood sugar collection with a particular gadget called a glucose screener or a home blood glucose meter. It requires a weak test of the blood, sometimes even from your fingertips, and measuring the aldose content in it.
Please follow the headline of your primary care physician to use your gadget with the most direct thanks.
Your primary care doctor can advise you once and is the best way to check your blood sugar. It should be recorded in a particular notepad, online device or application whenever you perform this operation. The time of day, continuous action, your last fete and various other factors will affect whether your primary care physician will worry about reading. Efforts to record applicable information in this way, such as:
What prescription and amount did you take?
What to eat, when to eat, or fast.
Assuming how many, anyhow extraordinary, and you are doing a lot of .exercises
In any case, this will help you and your primary care doctor check whether your treatment is effective.
Adequate supervision of one or more polygenic diseases can delay or frustrate the disorders that affect your eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Polygenic diseases can also pair your risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke. Fortunately, in the same way, the prevalence of blood sugar will reduce these problems.
Although the committee considers blood sugar to be too high, it is more likely to recommend low blood sugar levels, so your PCP may suggest higher goals.
Which regional unit has a regular normal blood sugar level reading?
The usual blood sugar level is 40 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L). At 2 hours, read 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) carefully to prove a polygenic infection. A close reading between 100 and 199 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L and 11.0 mmol/L) indicates the presence of prediabetes.
What is the standard blood sugar level for non-diabetics?
Most people with non-polygenic infections and blood sugar levels before dinner fluctuate around 70 to 80 mg/dL. For a couple, it is usually 60 years old; for others, ninety is the standard. Source: National Information Exchange for Polygenic Infections: "Your Diabetes Guide: Classify one of them as a pair."
What is the standard normal blood sugar level for one hour of eating?
The normal blood glucose range of the regional unit here, not the polygenic disease of the Raptor Polygenic Infection Association: rapid blood glucose (on the first day, eating on the previous day): less than 100 mg/dL. Dinner for one hour: 90 to 100 30 mg/dL. Several hours during dinner: 90 to 100 mg/dL.
What is the legal blood sugar level for caring for several diabetes?
Usually, less than one hundred and forty mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L). Analyze 100 to 199 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L and 11.0 mmol/L) of urea as pre-diabetes. When a polygenic disease is indicated within 2 hours, it should reach 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher.
Can diabetes be relieved?
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), prediabetes is reversible. Treatment can accept lifestyle changes, similar to eating fewer carbohydrates and exercising, and medication. If you may have prediabetes and cannot change your lifestyle, then you will create several polygenic infections within ten years as far as the clinic is concerned.
If my sugar is high, what should I eat?
Powers says that the seven nutrients in this area unit will encourage you to monitor blood sugar and keep you optimistic and make other sounds.
Rough, cooked or roasted vegetables. These can add colour, flavour and surface to the dinner. ...
vegetables. ...
Delicious low-calorie drink. ...
Melon or berry. ...
Whole grain, high fibre food. ...
a little fat. ...
Protein.
How do I prepare to lower my blood sugar levels quickly?
Exercise may be a quick and tangible thank you for lowering blood sugar levels. Exercise will lower your blood sugar for 24 hours or a lot when you finish exercising. This may be because it makes your body insignificant to a hypoglycemia specialist. Actual work makes the human body require aldose to supplement energy.
Is the sugar content of vi. three high?
Normally: A fast blood sugar level of fewer than 100 milligrams per litre (mg/dL) (5.6 millimoles per cubic meter (mmol/L)) is considered routine. Rapid blood glucose levels ranging from 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 7.0 mmol/L) are considered pre-diabetes. The current result is generally considered to be fast aldose hexose.
8.8 Is the normal blood sugar level high?
The body wants the blood's aldohexose level to remain between 4-7 mmol (standard level). Glucose levels higher than 8.0 millimolar are considered high, and extra time can damage veins, especially the gentler veins that carry blood to the eyes, heart, feet, and kidneys.
Is the 8.3 sugar level high?
In any case, in general, everyone’s target blood sugar level is essential: if you want to screen yourself – the standard target is 4-7mmol/l before admission and below 8-5-9mmol/l at dinner 2 hours. The chance of trying every few months is a small-the standard target is below 48mmol/mol (or vi.5% on the older estimate scale)
What is the standard blood sugar a few hours after eating?
What are the average blood glucose levels in the unit? However, if you are not admitted to the hospital (fasting) for at least eight hours, it is 100 mg/dL. More importantly, they are still 100 mg/dL after a few hours of consumption. During the day, basically before dinner, the level is usually kept to a minimum.
What happens if normal blood sugar level is too high?
If your blood sugar level is substantially too high, you will know:
Expanded thirst.
Continuous discharge.
Exhausted.
Quarrel and discharge.
Ed.
Stomachache.
Fruity tone.
Very dry.
Blood sugar is one hundred and sixty higher when eating?
Generally, high blood sugar (also known as "hyperglycemia") is considered "hyperglycemia" once it reaches 160 mg/dl or higher than your individual blood glucose goal. Make sure to increase your aid provider’s safety goals for your blood sugar before and during meals.
How long can you tolerate a pair of diabetes?
After estimating the impact of polygenic diseases on longevity, the researchers determined that in about 15 years of diagnosis, the diagnosis of polygenic diseases will be more mature, resulting in nearly 12 years of life loss. A 45-year-old diagnosis shortened life expectancy by about six years, while a 65-year-old diagnosis shortened life expectancy by two years.